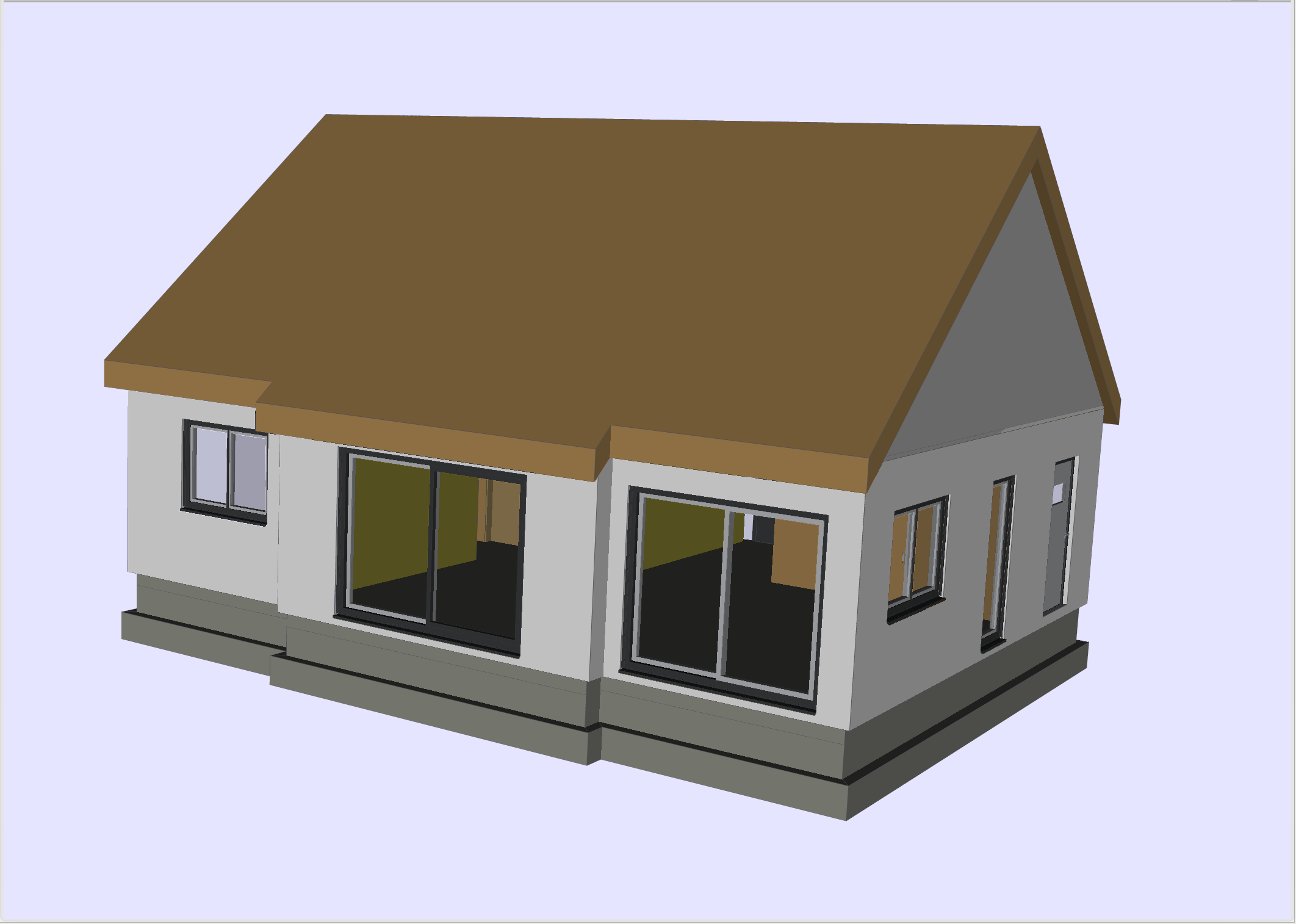
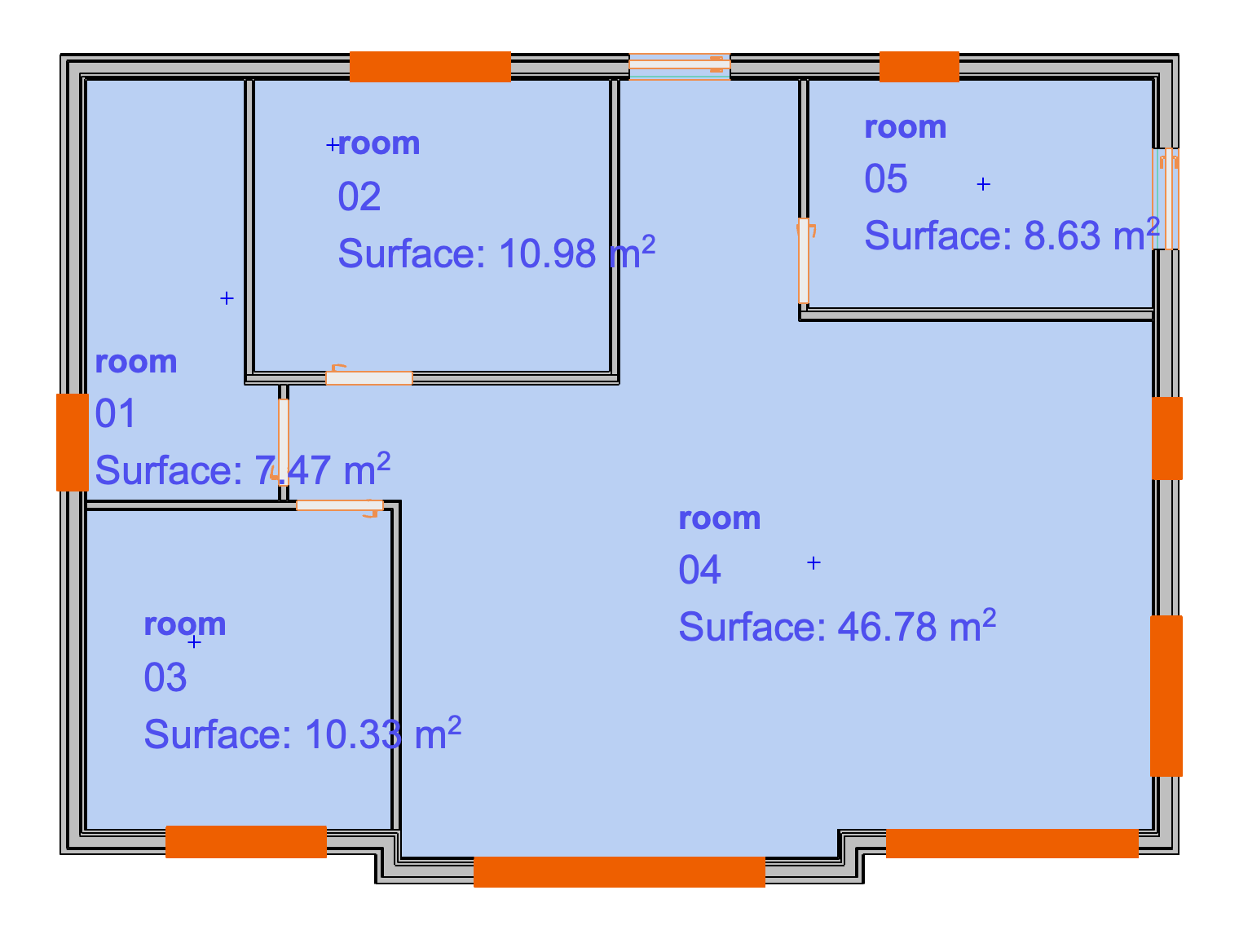
One story single family house
This test case deals with a one floor single family house.
1. Architecture
The studied building is composed of five rooms (a living room, 3 bedrooms and a bathroom?) for a gross floor area of around \(92 m^2\) and includes non-convertible attics (see Figure 1).
|
|
The house is a wood frame building. Its walls composition is as shown in Table 1. For the envelope walls, the material layers are listed from inside to outside.
Material |
Thickness [m] |
Conductivity \([\text{W}.\text{m}^{-1}.\text{K}^{-1}\)] |
Density \([\text{kg}.\text{m}^{-3}\)] |
Capacity \([\text{J}.\text{kg}^{-1}.\text{K}^{-1}\)] |
Envelope walls |
||||
Plasterboard |
0.013 |
0.25 |
900 |
1200 |
Cellulose |
0.14 |
0.23 |
800 |
2160 |
OSB |
0.012 |
0.15 |
600 |
1300 |
EPS |
0.06 |
0.05 |
10 |
1450 |
roughcast |
0.005 |
1.1 |
1950 |
1650 |
Partition walls |
||||
Plasterboard |
0.015 |
0.25 |
900 |
1200 |
Insulation |
0.07 |
0.035 |
1440 |
1400 |
Plasterboard |
0.015 |
0.25 |
900 |
1200 |
Floor |
||||
Reinforced concrete |
1.5 |
2300 |
2400 |
|
Ceiling |
||||
BA13 |
0.013 |
0.25 |
900 |
1200 |
OSB |
0.26 |
0.15 |
600 |
1300 |
The total glazed area of the house is around $25 m^2$, spread on its four facades as shown in Table 2.
Glazed construction |
Orientation |
Area \([\text{m}^2\)] |
Window 1 |
South |
2.45 |
Window 2 |
East |
2.45 |
Window 3 |
North |
0.83 |
Window 4 |
North |
2.45 |
Window 5 |
West |
1.03 |
Bay window 1 |
South |
7.30 |
Bay window 2 |
South |
6.33 |
Door window 1 |
East |
2.07 |
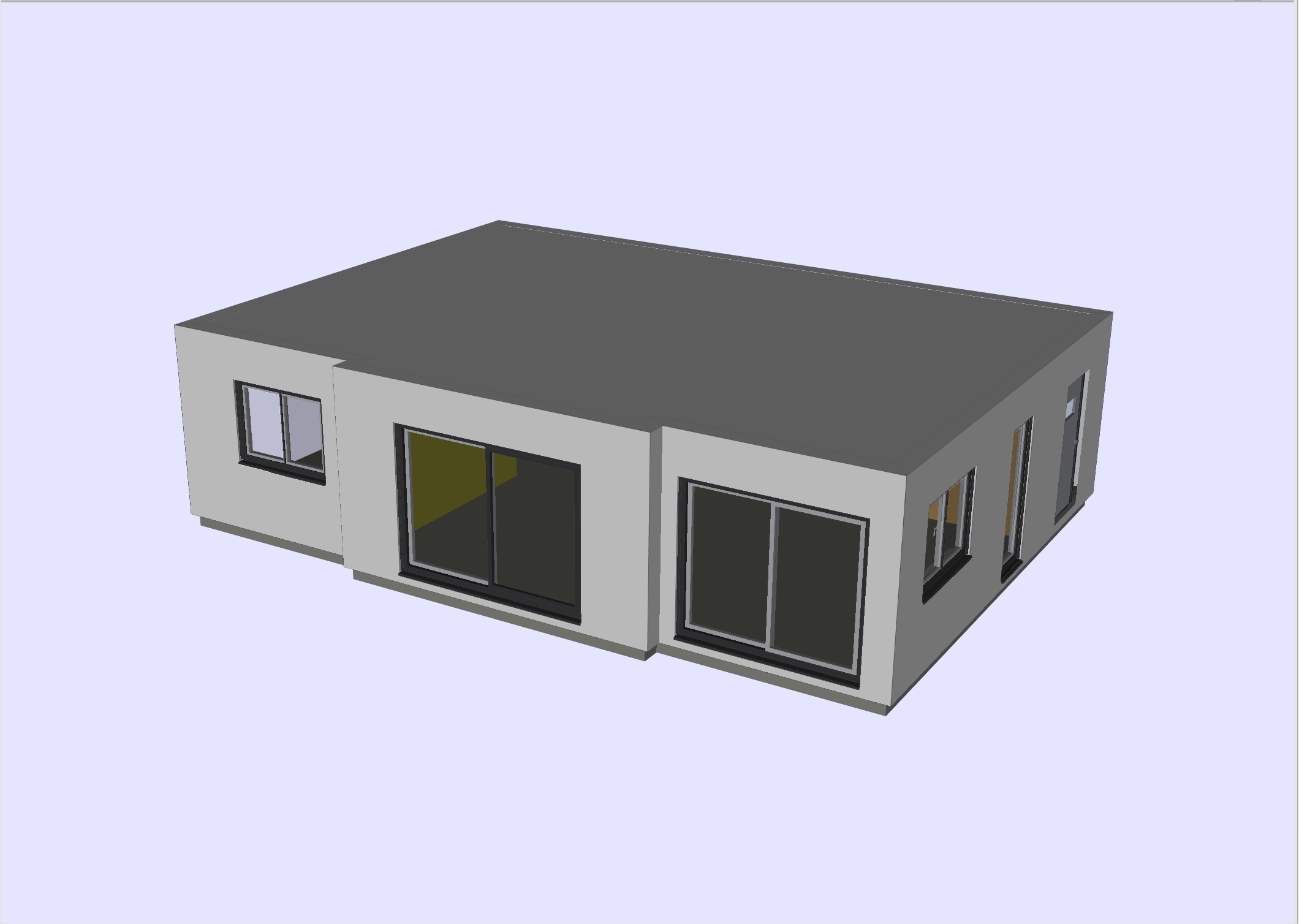
2. Flat roof
In this example, we limit our study to the first floor and model the tilted roof as a flat one (see Figure 2). Its roof-to-roof height is \(2.5 m^2\).
| This example is only for the validation of the developed toolchain. We are aware that the geometry simplification applied to the roof may lead to important discrepancies in the simulation results. |

 .pdf
.pdf